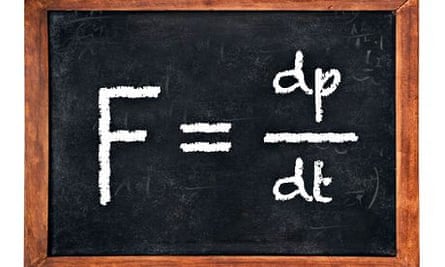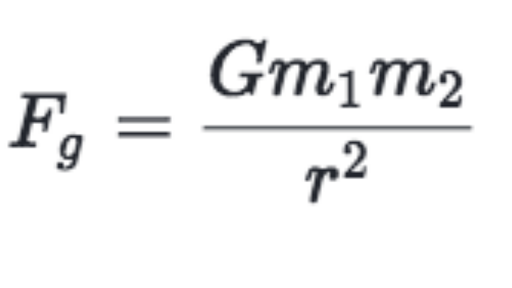Mathematically it describes the causes and effects of force and changes in motion of an object.
State newton s second law of motion and derive formula of force.
The si unit of force is newton n.
1 newton s 1 st law.
Descartes laws are very similar to newton s first law of motion.
Second law of motion formula.
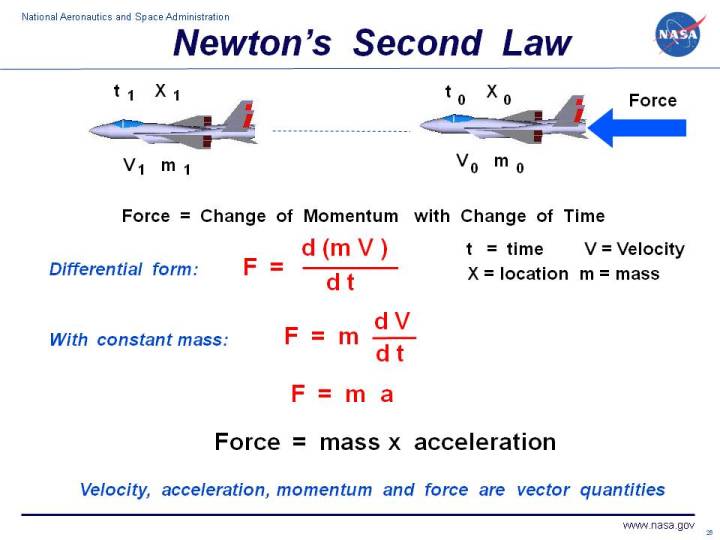
Let us assume that we have a car at a point 0 defined by location x 0 and.
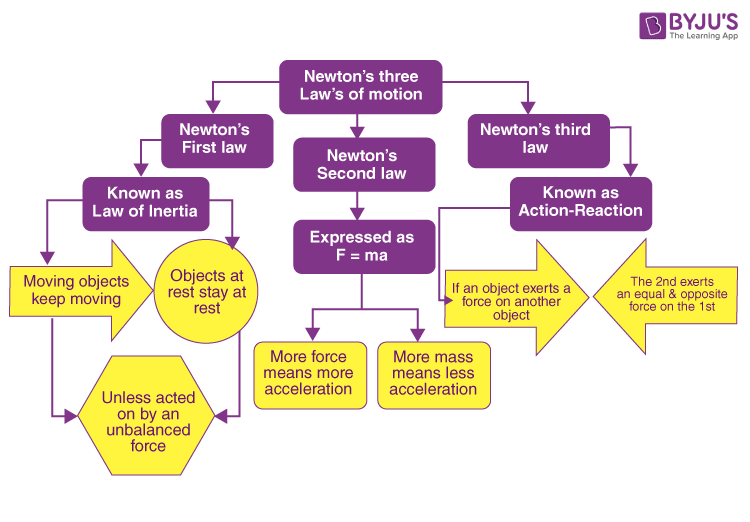
Often expressed as the equation a fnet m or rearranged to fnet m a the equation is probably the most important equation in all of mechanics.
Before understanding the equation of newton s second law of motion which deals with force mass and acceleration of an object let s have a look upon the three laws of motion.
A force of 1n is explained as.
Newton s second law says that when a constant force acts on a massive body it causes it to accelerate.
Newton s second law states that the magnitude of the net external force on an object is f net ma.
It is also called the.
It is used to predict how an object will accelerated magnitude and direction in the presence of an unbalanced force.
Deriving newton s second law.
Newton s first law states that if a body is at rest or moving at a constant speed in a straight line it will remain at rest or keep moving in a straight line at constant speed unless it is acted upon by a force this postulate is known as the law of inertia the law of inertia was first formulated by galileo galilei for horizontal motion on earth and was later generalized by rené descartes.
A force of 1n acting on the body with mass 1kg and producing an acceleration of 1m s 2.
Newton s second law of motion can be formally stated as follows.
Newton s second law describes the affect of net force and mass upon the acceleration of an object.
Newton s second law of motion.
Newton s second law is also referred to as the real law because the other two laws can be explained with the help of the second law.
Newton s second law for rotation latex sum i tau i i alpha latex says that the sum of the torques on a rotating system about a fixed axis equals the product of the moment of inertia and the angular acceleration.
The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force in the same direction as the net force and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
This is the rotational analog to newton s second law of linear motion.
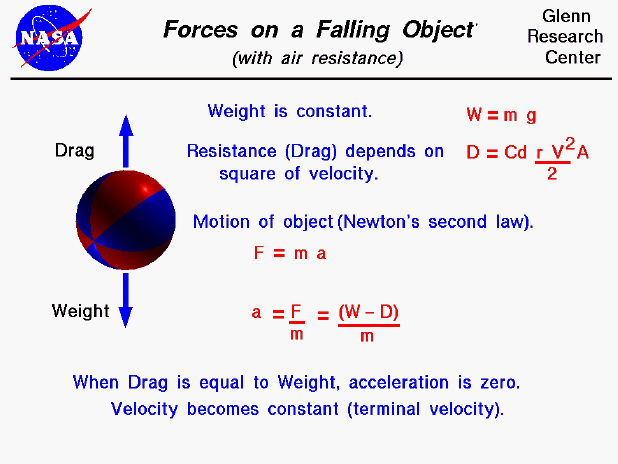
Using galileo s result and newton s second law we can derive an equation for weight.
It experiences only the downward force of gravity which has magnitude w.