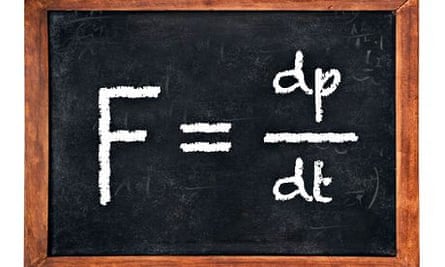Newton s second law states that the net force applied on the body is equal to the rate of change in its momentum.
State newton s 2nd law of motion and derive its mathematical expression.
Derive relation f ma from newton 2nd law of motion let us derive the relation of force f ma from newton s second law.
F ma or f m v u t or ft mv mu that is when f 0 v u for whatever time t.
According to the newton s 2 nd law of motion the rate of change of linear momentum of a body is directly proportional to the applied external force and in the direction of force.
Consider two colliding particles a and b whose masses are m1 and m2 with initial and final velocities as u 1 and v 1 of a and u 2 and v 2 of b.
That situation is described by newton s second law of motion.
The mathematical expression is given by.
Newton s third law of motion states that every action has equal and opposite reaction.
Newton s laws of motion are three physical laws that together laid the foundation for classical mechanics they describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it and its motion in response to those forces.
The second law of motion is used to validate this phenomenon.
In this section we shall learn about the formulation of the second law of motion.
Derivation of conservation of momentum.
With these examples we can conclude that the impact produced by an object depends on its mass and velocity i e its momentum and the time rate at which the change in momentum is occurring.
For a constant mass force equals.
The law of conservation of momentum is an important consequence of newton s third law of motion.
In other words the state of motion of a body changes only on application of a net non zero force.
More precisely the first law defines the force qualitatively the second law offers a quantitative measure of the force and the third asserts that a single isolated.
Derivation of newton s first law of motion from newton s second law of motion newton s first law states that a body stays at rest if it is at rest and moves with a constant velocity if already moving until a net force is applied to it.
If f ab is a force of body a acting on b and f ba is force by b on body a.